In April 2014, the Singapore NEA has updated the PSI calculation to also include PM2.5. http://www.nea.gov.sg/anti-pollution-radiation-protection/air-pollution-control/psi
W związku z niedawnym smogiem z Azji Południowo-Wschodniej z Indonezji, który dotknął Singapur, a obecnie Malezję , otrzymaliśmy wiele pytań o to, dlaczego istnieje różnica między danymi, które można odczytać na stronie internetowej Singapurskiej NEA ( nea.gov.sg ) a projektem Światowego Indeksu Jakości Powietrza w Singapurze Strona internetowa .
Na przykład oto, co można dziś przeczytać na stronie internetowej NEA:
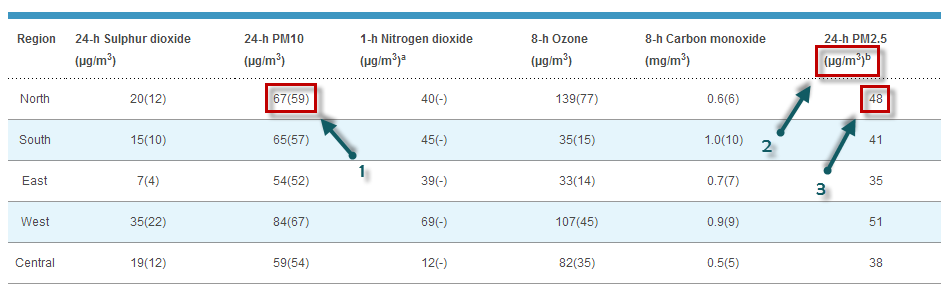
Z jakiegoś historycznego powodu Singapur stosuje PSI ( wskaźnik standardowy zanieczyszczeń ) do oceny jakości powietrza. Na powyższym obrazku liczba 1 odpowiada wartości PM10 używanej do oceny PSI. Wartość 67(/59) można odczytać jako 67 μg/m3, co odpowiada PSI wynoszącemu 59. PSI ocenia się jako maksimum indywidualnego PSI dla każdej z substancji zanieczyszczających: PM 10 , SO 2 , NO 2 , O 3 (Ozon) i CO 2 .
PSI(Singapore-North) = max( PSIPM10-based, ... PSIO3-based )= max (59, ..., 77) = 77
To powiedziawszy, interesującą rzeczą jest to, że w tej samej tabeli dane dotyczące PM2,5 są również podane w ostatniej kolumnie (patrz 3). Dane te podawane są wyłącznie w μg/m3 (patrz 2) i nie są przeliczane na coś takiego jak PSI (tj. konwersja masy PM2,5 na wskaźnik zanieczyszczenia lub jakości). Ta konwersja jednak istnieje i jest zdefiniowana przez Agencję Ochrony Środowiska Stanów Zjednoczonych . Najłatwiejszym sposobem przeliczenia jest skorzystanie z kalkulatora internetowego dostępnego na stronie airnow.gov :
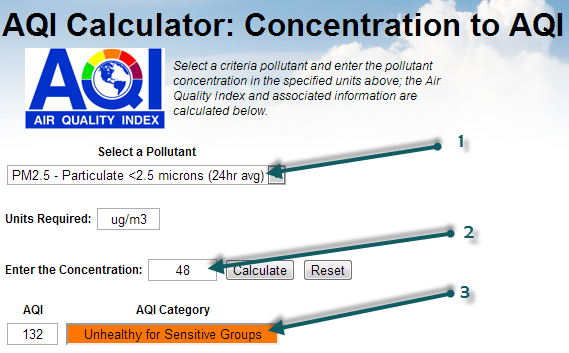
If you select the PM2.5 (1), then enter the mass concentration of 48 (2), can click on Calculate, you will obtain the AQI of 132 (3). So, based on the PM2.5 AQI conversion, the PSI that is used for Singapore could be extended (let's call it PSI++) to also take into account the PM2.5 information. In which case, the PSI++ would be the maximum of the regular PSI (based on PM10 only) and the PM2.5 AQI:
PSI++ = max( PSI, AQIPM.25 ) = max( 77, 132 ) = 132
This PSI++, that is commonly referred as AQI (or Air Quality Index), is what is being used on the the World Air Quality Index project, for all the cities (provided PM2.5 is available for the city). And this explains why the values are different between the NEA website and the World Air Quality Index project.
Moreover, when doing the convertion, make sure you use the 1-hour reading for the PM2.5 concentration rather than the 24-hours averaged value, as shown on the below image:
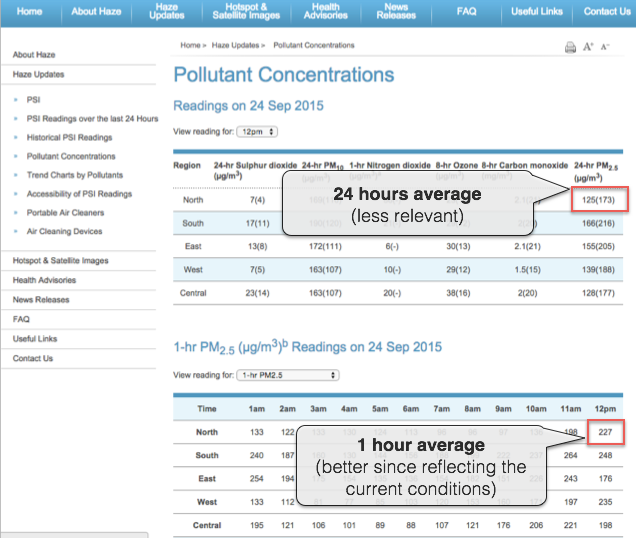
http://www.haze.gov.sg/haze-updates/pollutant-concentrations/type/PM25-1Hr
If you want to know more about PM10 vs PM2.5, and especially why PM10 is still used, please check the faq entry about why is PM2.5 often higher than PM10? Is PM10 still a relevant measure?
--
For more information about specific countries or continent, please refer to those articles: Thailand and Malysia - India - China - Hong Kong / Canada (Air Quality Health Index) - South America - Australia - Quebec and Montreal - Singapore - Poland - Indonesia .
For information about the 24 hours averaging used or Ozone and Particulate Matter (PM2.5), please refer to those two articles: Ground Ozone Index - PM2.5 Instant Cast
