In April 2014, the Singapore NEA has updated the PSI calculation to also include PM2.5. http://www.nea.gov.sg/anti-pollution-radiation-protection/air-pollution-control/psi
Con el reciente smog del sudeste asiático proveniente de Indonesia que afecta a Singapur y ahora a Malasia , tenemos muchas preguntas sobre por qué hay una diferencia entre los datos que se pueden leer en el sitio web de la NEA de Singapur ( nea.gov.sg ) y el proyecto del Índice Mundial de Calidad del Aire de Singapur. Página web .
Por ejemplo, esto es lo que se puede leer hoy en el sitio web de la NEA:
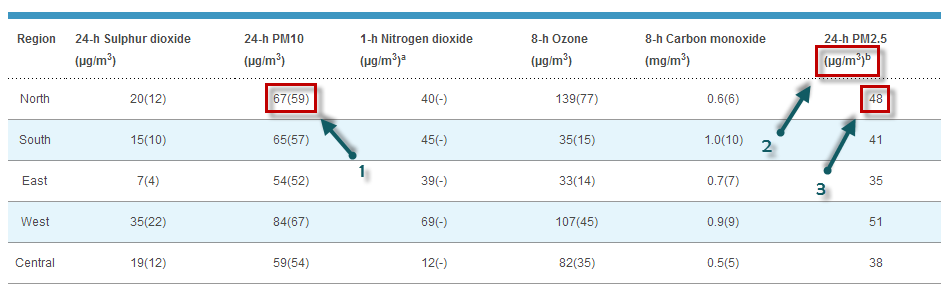
Por alguna razón histórica, Singapur utiliza el PSI ( índice estándar de contaminantes ) para evaluar la calidad del aire. En la imagen de arriba, el número 1 corresponde al valor de PM10 que se utiliza para la evaluación de PSI. El valor 67(/59) se puede leer como 67 μg/m3, correspondiente a un PSI de 59. El PSI se evalúa como el máximo del PSI individual para cada uno de los contaminantes: PM 10 , SO 2 , NO 2 , O 3 (Ozono) y CO 2 .
PSI(Singapore-North) = max( PSIPM10-based, ... PSIO3-based )= max (59, ..., 77) = 77
Dicho esto, lo interesante es que, en esta misma tabla, el dato de PM2,5 también se proporciona en la última columna (ver 3). Estos datos se proporcionan únicamente en μg/m3 (ver 2) y no hay conversión a algo como el PSI (es decir, una conversión de la masa de PM2,5 a un índice de contaminación o calidad). Sin embargo, esta conversión existe y está definida por la Agencia de Protección Ambiental de EE. UU . La forma más sencilla de realizar la conversión es utilizar la calculadora en línea, disponible en airnow.gov :
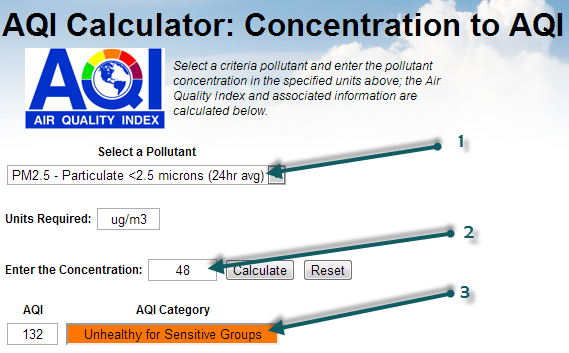
If you select the PM2.5 (1), then enter the mass concentration of 48 (2), can click on Calculate, you will obtain the AQI of 132 (3). So, based on the PM2.5 AQI conversion, the PSI that is used for Singapore could be extended (let's call it PSI++) to also take into account the PM2.5 information. In which case, the PSI++ would be the maximum of the regular PSI (based on PM10 only) and the PM2.5 AQI:
PSI++ = max( PSI, AQIPM.25 ) = max( 77, 132 ) = 132
This PSI++, that is commonly referred as AQI (or Air Quality Index), is what is being used on the the World Air Quality Index project, for all the cities (provided PM2.5 is available for the city). And this explains why the values are different between the NEA website and the World Air Quality Index project.
Moreover, when doing the convertion, make sure you use the 1-hour reading for the PM2.5 concentration rather than the 24-hours averaged value, as shown on the below image:
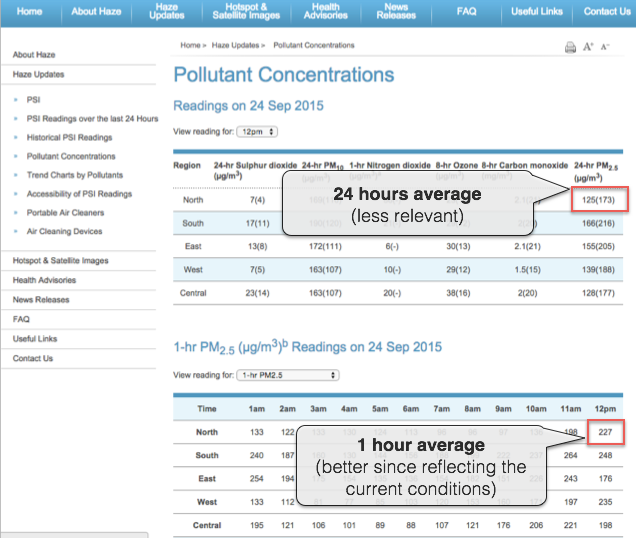
http://www.haze.gov.sg/haze-updates/pollutant-concentrations/type/PM25-1Hr
If you want to know more about PM10 vs PM2.5, and especially why PM10 is still used, please check the faq entry about why is PM2.5 often higher than PM10? Is PM10 still a relevant measure?
--
For more information about specific countries or continent, please refer to those articles: Thailand and Malysia - India - China - Hong Kong / Canada (Air Quality Health Index) - South America - Australia - Quebec and Montreal - Singapore - Poland - Indonesia .
For information about the 24 hours averaging used or Ozone and Particulate Matter (PM2.5), please refer to those two articles: Ground Ozone Index - PM2.5 Instant Cast
