In April 2014, the Singapore NEA has updated the PSI calculation to also include PM2.5. http://www.nea.gov.sg/anti-pollution-radiation-protection/air-pollution-control/psi
Con il recente smog del sud-est asiatico proveniente dall'Indonesia che ha colpito Singapore e ora la Malesia , abbiamo molte domande sul perché esiste una differenza tra i dati che possono essere letti dal sito web NEA di Singapore ( nea.gov.sg ) e il progetto World Air Quality Index di Singapore. pagina web .
Ad esempio, ecco cosa si può leggere oggi nel sito della NEA:
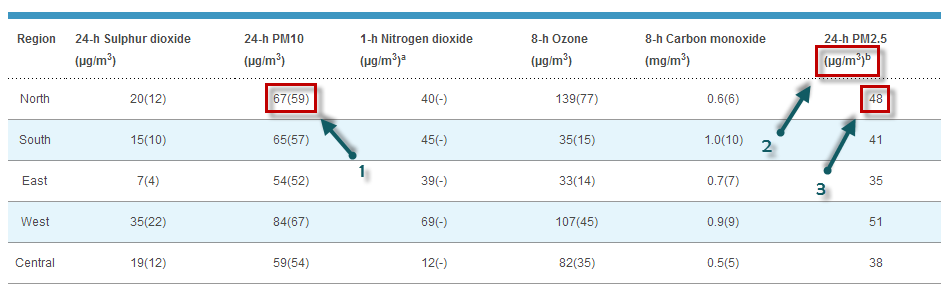
Per qualche ragione storica, Singapore utilizza il PSI ( Polutant Standard Index ) per valutare la qualità dell'aria. Nell'immagine sopra, il numero 1 corrisponde al valore PM10 utilizzato per la valutazione PSI. Il valore 67(/59) può essere letto come 67 μg/m3, corrispondente ad un PSI di 59. Il PSI viene valutato come il massimo del singolo PSI per ciascuno degli inquinanti: PM 10 , SO 2 , NO 2 , O 3 (Ozono) e CO 2 .
PSI(Singapore-North) = max( PSIPM10-based, ... PSIO3-based )= max (59, ..., 77) = 77
Detto questo, la cosa interessante è che, in questa stessa tabella, i dati del PM2,5 sono riportati anche nell’ultima colonna (vedi 3). Questi dati sono forniti solo in μg/m3 (vedi 2) e non è prevista alcuna conversione in qualcosa di simile al PSI (ovvero una conversione dalla massa PM2,5 a un indice di inquinamento o di qualità). Questa conversione però esiste ed è definita dalla US Environmental Protection Agency . Il modo più semplice per eseguire la conversione è utilizzare il calcolatore online, disponibile su airnow.gov :
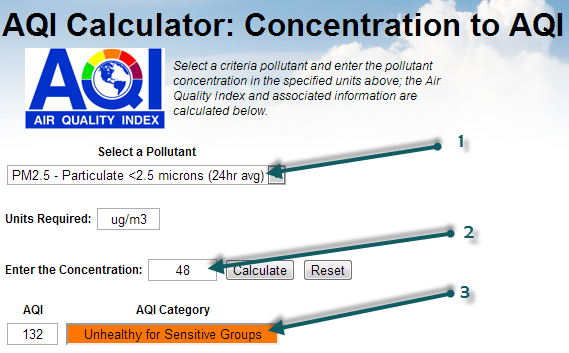
If you select the PM2.5 (1), then enter the mass concentration of 48 (2), can click on Calculate, you will obtain the AQI of 132 (3). So, based on the PM2.5 AQI conversion, the PSI that is used for Singapore could be extended (let's call it PSI++) to also take into account the PM2.5 information. In which case, the PSI++ would be the maximum of the regular PSI (based on PM10 only) and the PM2.5 AQI:
PSI++ = max( PSI, AQIPM.25 ) = max( 77, 132 ) = 132
This PSI++, that is commonly referred as AQI (or Air Quality Index), is what is being used on the the World Air Quality Index project, for all the cities (provided PM2.5 is available for the city). And this explains why the values are different between the NEA website and the World Air Quality Index project.
Moreover, when doing the convertion, make sure you use the 1-hour reading for the PM2.5 concentration rather than the 24-hours averaged value, as shown on the below image:
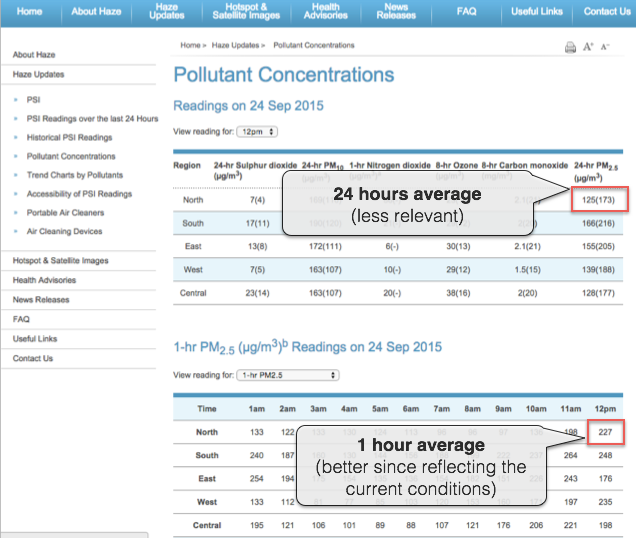
http://www.haze.gov.sg/haze-updates/pollutant-concentrations/type/PM25-1Hr
If you want to know more about PM10 vs PM2.5, and especially why PM10 is still used, please check the faq entry about why is PM2.5 often higher than PM10? Is PM10 still a relevant measure?
--
For more information about specific countries or continent, please refer to those articles: Thailand and Malysia - India - China - Hong Kong / Canada (Air Quality Health Index) - South America - Australia - Quebec and Montreal - Singapore - Poland - Indonesia .
For information about the 24 hours averaging used or Ozone and Particulate Matter (PM2.5), please refer to those two articles: Ground Ozone Index - PM2.5 Instant Cast
